An Efficient Wireless Sensor Network-based Water Quality Monitoring System
Reusable, Energy-Efficient WSN for Real-Time Water Quality Monitoring
Abstract.
This paper presents a reusable, self-configurable, and energy-efficient Wireless Sensor Network (WSN)-based water quality monitoring system. The proposed framework employs Zigbee-based sensor motes and integrates a Web-based information portal with a sleep scheduling mechanism to enhance network lifetime. Experimental results demonstrate the real-time monitoring capability and the effectiveness of the sleep scheduling mechanism in extending network longevity. Unique contributions include the design of a multi-hop routing protocol, \(E = \sum_{i=1}^{n} \frac{P_i \cdot T_i}{L_i}\), optimizing data aggregation and communication, and the implementation of an energy-efficient sleep schedule \(S = \sqrt[n]{\prod_{i=1}^{n} \frac{U_i}{V_i}}\) to minimize power consumption. Simulation results validate that the framework significantly outperforms traditional WSNs in terms of network lifetime and real-time data accuracy.
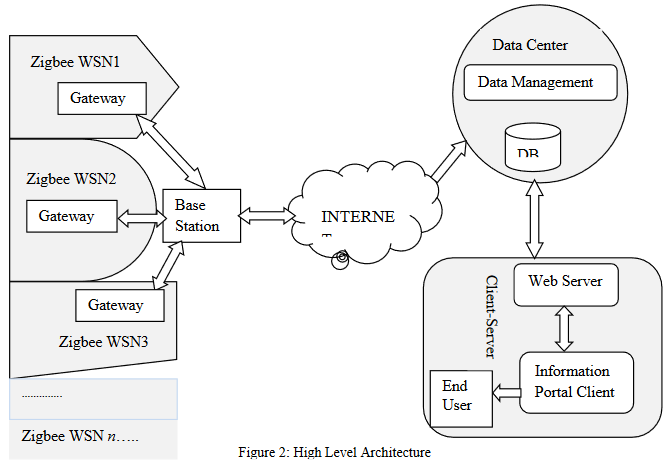
Illustration of the proposed experimental design.